

In a paper published in the journal Science, researchers from the University of Washington School of Medicine stated that after 25 postmenopausal female obese diabetic patients supplemented with 250 mg of NMN daily for 10 weeks, their muscle insulin sensitivity was enhanced, and the adult The number of myocytes increases and the regenerative capacity of skeletal muscles improves.

In this study, 25 obese postmenopausal women with diabetes were recruited, and 12 subjects were randomly assigned to the placebo group, and 13 subjects were assigned to the NMN group (oral NMN 250 mg/day). Subsequently, the researchers conducted health tests on the subjects, including fat mass, blood pressure, insulin and other indicators, and repeated the tests on the above indicators after 10 weeks.
It was found that after supplementing NMN for 10 weeks, compared with the subjects of the placebo group, the concentration of NMN metabolites in the plasma of the subjects of the NMN group increased by about 3 times. And the NAD+ level in the blood of the subjects was significantly increased by about 30%. This shows that NMN supplementation can be absorbed and metabolized by the body, and can increase the NAD+ level in the subject.
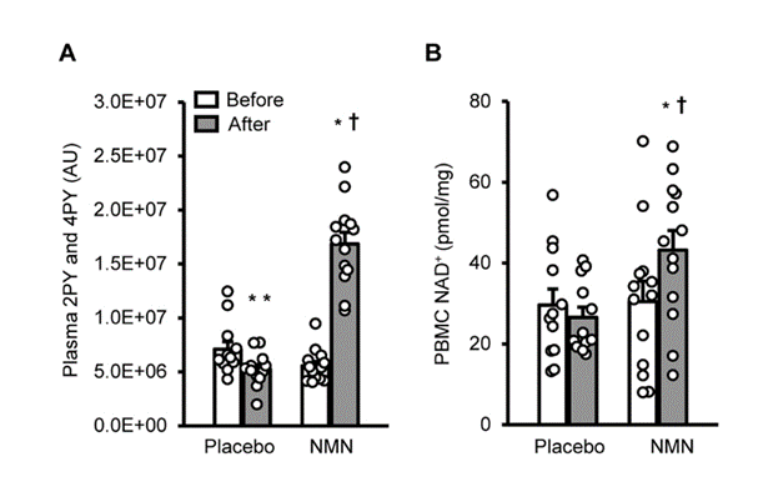
Figure 1 The levels of NMN-related metabolites in plasma and NAD+ levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells
In addition, the researchers found that there were no differences in fat mass, intrahepatic triglyceride content, blood pressure, plasma glucose, free fatty acids, and lipids between the NMN group and the placebo group, all within the normal range . However, compared with the placebo group, subjects in the NMN group showed an increase in muscle insulin sensitivity of approximately 25%.
Subsequently, the researchers detected the overall gene expression of the subjects' quadriceps muscle samples by RNA sequencing to assess the effect of NMN supplementation on the muscles.
It was found that 308 genes were differentially expressed during insulin injection in subjects supplemented with NMN compared with before NMN supplementation. Through further analysis of differential genes, it was found that most of the differential genes were related to platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF). Platelet-derived growth factor can promote cell growth. For example, when the liver is damaged, platelet-derived growth factor will be synthesized and released, thereby promoting cell regeneration and accelerating tissue wound repair.
The researchers found that the expression levels of genes related to platelet-derived growth factor were significantly increased in the skeletal muscle of subjects in the NMN group during insulin injection. This suggests that NMN supplementation increases gene expression levels of platelet-derived growth factor, thereby increasing the number of myoblasts in skeletal muscle.
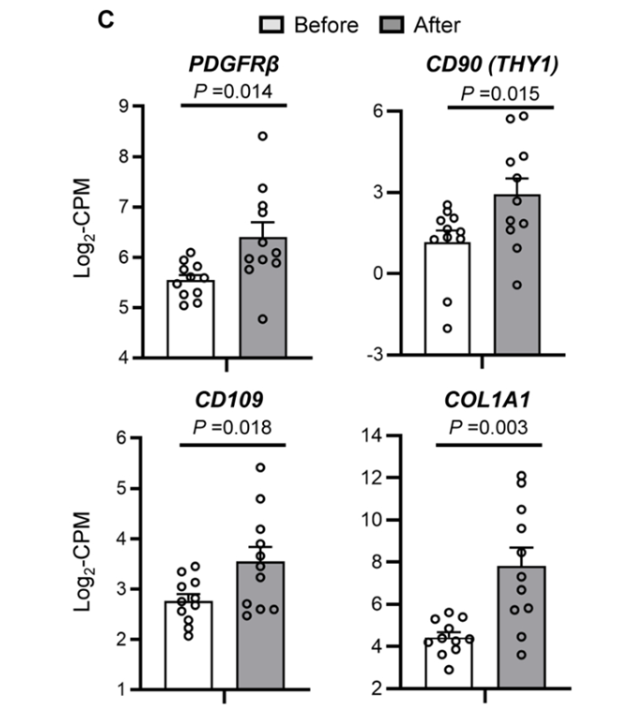
Figure 2 Effects of NMN supplementation on insulin sensitivity and signal transduction in skeletal muscle
In conclusion, this randomized, double-blind human trial showed that after 10 consecutive weeks of daily supplementation of 250 mg of NMN in obese postmenopausal women with diabetes, their muscle insulin sensitivity increased by about 25%, which was comparable to weight loss of 10% % or using the insulin sensitizer troglitazone for 12 weeks showed similar improvement. In addition, NMN supplementation can also increase the number of myoblasts in the subjects' skeletal muscles, thereby improving the regenerative capacity of skeletal muscles. But "the mechanisms responsible for these metabolic effects await further investigation," the researchers said.
